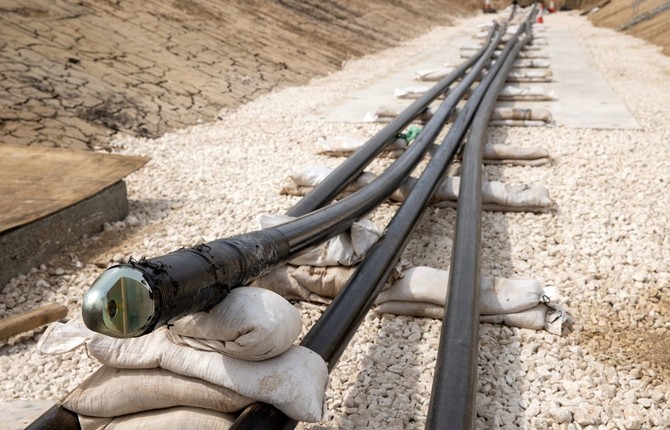
National Grid’s new interconnector, Viking Link, has been switched on, with the 475 mile link having a capacity of 1.4GW.
The £1.7 billion land and subsea link between the UK and Denmark joins Bicker Fen substation in Lincolnshire with Revsing substation in southern Jutland, Denmark, the longest of its type in the world.
A joint venture between National Grid and Danish System Operator, Energinet, work on the link started in 2019, with more than four million working hours spent to get to this point.
National Grid’s interconnector business is run by National Grid Ventures (NGV), which operates outside of National Grid’s core regulated businesses in the UK and US. NGV develops, operates and invests in energy projects, technologies and partnerships to accelerate the development of our clean energy future.
Viking Link will bring huge benefits for UK consumers including cheaper, lower carbon power and increased energy security as the UK can call on additional power from Denmark when needed.
National Grid launched the UK’s first interconnector (IFA) to France in 1986. Since then, it has built five more including a second link with France (IFA2) and further connections with The Netherlands (BritNed), Belgium (Nemo Link) and Norway (North Sea Link).
By 2030 National Grid expects at least 90 per cent of the energy imported through the company’s interconnectors will be from zero carbon energy sources.
Earlier in 2023 National Grid announced joint plans with TenneT for a new 1.8GW interconnector between the UK and The Netherlands, called LionLink. The link would not only join the two countries but also connect to offshore wind generation. LionLink would be the second link between the two countries and is expected to be operational in the early 2030s. A second new link called Nautilus, is also in the planning phase with the potential to connect with Belgium.
Latest News
-
DPD aims to raise £200,000 to grant wishes to 100 critically ill children
-
Training provider hands 20 charities grants to boost skills in their communities
-
Law firm links up with NGO body to support charities
-
Marks & Spencer donates 100m meals to good causes over last decade
-
Jewellers body offers grants of up to £50,000 to boost training
-
Agency overhauls community charity’s brand for free
© 2019 Perspective Publishing Privacy & Cookies








Recent Stories